The electric potential V at any point (x, y,z), all in meters in space is given by V = 4x2 volt. The electric field at the point(1, 0, 2) in volt/meter is
-
Solution

A square surface of side L meter in the plane of the paper is placed in a uniform electric field E(volt/m) acting along the same plane at an angle θ with the horizontal side of the square as shown in Figure. The electric flux linked to the surface, in units of volt. m, is

-
Solution
Electric flux, φ= EA cos θ, where θ
= angle between E and normal to the surface.
Here θ=π⁄2
⇒ φ = 0
Two positive ions, each carrying a charge q, are separated by a distance d. If F is the force of repulsion between the ions, the number of electrons missing from each ion will be(e being the charge of an electron)
-
Solution

The electric intensity due to a dipole of length 10 cm and having a charge of 500 mC, at a point on the axis at a distance 20 cm from one of the charges in air, is
-
Solution

If a charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges Q such that the system is in equilibrium then the value of q is
-
Solution


An uncharged sphere of metal is placed in between charged plates as shown. The lines of force look like
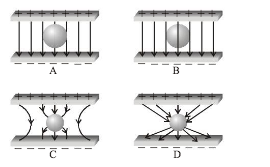
-
Solution
Electric lines of force never intersect the conductor.They are perpendicular and slightly curved near the surface of conductor.
A solid conducting sphere of radius a has a net positive charge 2Q. A conducting spherical shell of inner radius band outer radius c is concentric with the solid sphere and has a net charge – Q.The surface charge density on the inner and outer surfaces of the spherical shell will be

-
Solution
Electric lines of force never intersect the conductor.They are perpendicular and slightly curved near the surface of conductor.
A glass rod rubbed with silk is used to charge a gold leaf electroscope and the leaves are observed to diverge. The electroscope thus charged is exposed to X-rays for a short period. Then
-
Solution
Charge on glass rod is positive, so charge on gold leaves will also be positive.Due to X-rays, more electrons from leaves will be emitted, so leaves becomes more positive and diverge further.
A solid sphereical conductor of radius R has a spherical cavity of radius a (a < R) at its centre. A charge + Q is kept at the centre. The cahrge at the inner surface, outer and at a positionr (a < r < R) are respectively
-
Solution

The charge at the inner surface, outer surface and inside the conductor at P= (– Q, +Q, 0) as shown in the figure
The electrostatic potential (φr) of a spherical symmetric system kept at origin, is shown in the figure, and given as

Which of the following option(s) is/are incorrect
a. For spherical region r ≤ R0 total electrostatic energy stored is zero
b. Within r = 2R0 total charge is q.
c. There will be no charge anywhere except at r =R0
d. None of these
-
Solution
(a, b, c, d)
The potential shown is for charged spherical conductor.





