Attempted
Correct
UnAttempted
Wrong
The maximum kinetic energy (Emax) of photoelectrons emitted in a photoelectric cell varies with frequency (v) as shown in the graph. The slope of the graph is equal to

Einstein’s photoelectric equation is Ek = hv – φ. In this equation Ek refers to
The maximum velocity of an electron emitted by light of wavelength λ incident on the surface of a metal of work-function φ is
![]()
The velocity of a body of rest mass mo is √3⁄2c (where c is the velocity of light in vacuum). The mass of this body is:
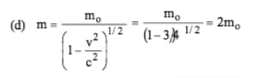
4eV is the energy of incident photon and the work function is 2eV. The stopping potential will be

Einstein’s work on photoelectric effect provided support for the equation
Einstein’s photo electric effect & compton effect established particle nature of light. These effects can be explained only, when we assume that the light has particle nature (To explain, Interference & Diffraction the light must have wave nature. It means that light has both particle and wave nature, so it is called dual nature of light)
The photoelectric work function for a metal surface is 4.125 eV. The cut-off wavelength for this surface is

A particle with rest mass m0 is moving with speed of light c.The de-B roglie wavelength associated with it will be
![]()
A proton and α-particle are accelerated through the same potential difference. The ratio of their de-B roglie wavelength will be

In a photoelectric experiment the stopping potential for the incident light of wavelength 4000 Å is 2 volt. If the wave length be changed to 3000 Å, the stopping potential will be
![]()